Migratory flyways
· Totally
9
India
(3) - Central Asian Flyway (entire India), East Asian - Australasian flyway,
West Asian - East African Flyway
Bird Life International
·
It
is a Global Partnership of Non Governmental Conservation Organizations.
·
It
identifies the sites known/ referred to as ‘Important Bird and Biodiversity
Areas’.
· Headquartered at Cambridge UK.
Important Bird Areas
·
The
Bombay Natural History Society and Birdlife International have identified more
than 450 Important Bird Areas in India. Forty percent of these IBAs fall
outside the Protected Area network and thus form an important tool for
landscape-level conservation planning.
Important bird sanctuaries
·
Sandi
Bird Sanctuary - UP
·
Ranganathittu
Bird Sanctuary - Karnataka
·
Mayani
Bird Sanctuary - Maharashtra
·
Velavadar
Bird Sanctuary – Gujarat
·
Atapaka
bird sanctuary – AP - world’s largest home for spot-billed pelicans
·
Nelapattu
bird sanctuary – AP - biggest habitats for some hundreds of pelicans and
greater flamingos (Annual Flamingo festival)
o
North
of Pulicat lake
Important birds
·
Gulf
of Kutch National Park - Western Reef Heron
·
Mahatma
Gandhi National Park (Port Blair in South Andaman) - White Bellied Sea Eagle
·
Malvan
Wildlife Sanctuary (Maharashtra) - Sarus Crane - Tallest flying bird of the
world
Thattekad Bird Sanctuary: (Kerala)
·
First
bird Sanctuary in Kerala
·
Salim
Ali, one of the best-known ornithologists, described this sanctuary as the
richest bird habitat on peninsular India.
·
Thattekkad
literally means flat forest, and the region is an evergreen low-land forest
located between the branches of the Periyar River.
Nagi and Natki bird sanctuaries: (Bihar)
·
Bihar’s
first state-level bird festival ‘Kalrav’ will be held at the world-famous
Nagi-Nakti bird sanctuaries from January 15, 2021.
World Wetlands Day
·
World
Wetlands Day is celebrated every year on 2nd February.
·
Smallest
Ramsar site - Renuka Wetland in Himachal Pradesh;
·
Largest
Ramsar Site - Sunderbans in West Bengal; Second Largest Ramsar site - Vembanad
Lake in Kerala
·
The
central government recently announced the establishment of a Centre for Wetland
Conservation and Management (CWCM) as a part of the National Centre for
Sustainable Coastal Management, the first of its kind, in India.
·
Ramsar
convention was signed in 1971 on 2nd Feb by UNESCO and came into force in 1975.
Not legally binding.
·
India
joined the convention in 1982.
·
IUCN
provides the administrative services to the Convention on Wetlands.
·
It
is the only global treaty to focus on a single ecosystem.
·
Ramsar
Convention criteria
o
Any
land saturated with water whether permanent or temporary, natural or
artificial, static or flowing water, freshwater, saltwater or brackish water,
marshland or swamp land, peat land (organic matter is partially decomposed) –
but depth not exceeding 6 m.
o
It
has hydric soil that is saturated with water for long period so that the upper
layer becomes anaerobic
o
It
should support hydrophytic vegetation
o
Dam,
paddy field, lake
·
80
Ramsar Sites in India as of March 2024 - Tamil Nadu (16) and Uttar Pradesh (10)
·
Recent
Ramsar sites
o
designated
in January 2024
§ Ankasamudra Bird Conservation
Reserve – Karnataka
§ Aghanashini Estuary – Karnataka
§ Magadi Kere Conservation Reserve –
Karnataka
§ Karaivetti Bird sanctuary – Tamil
Nadu
§ Longwood Shola Reserve Forest –
Tamil Nadu
o
Designated
in 2022
§ Hygam Wetland Conservation Reserve –
Jammu and Kashmir
§ Shallbugh Wetland Conservation
Reserve – Jammu and Kashmir
§ Thane Creek – Maharashtra
Important Ramsar Sites
·
Uttarakhand
– Asan Barrage
·
Tripura
– Rudrasagar lake
·
Mizoram
– Pala Wetland
·
Manipur
– Loktak lake
·
Andhra
Pradesh – Kolleru Lake
·
Assam
– Deepor Beel
·
Bihar
– Kanwar lake
·
Goa
– Nanda Lake
·
Haryana
- Sultanpur National Park, Bhindawas Wildlife Sanctuary
·
Ladakh
- Tso Kar, Tso Moriri Lake
·
Rajasthan
- Keoladeo National Park, Sambhar Lake
·
West
Bengal - East Kolkata Wetlands, Sundarban Wetland
·
Himachal
Pradesh - Chandra Taal, Pong Dam Lake, Renuka Lake
·
Kerala
- Ashtamudi Wetland, Sasthamkotta Lake, Vembanad-Kol Wetland (Kole and Kuttanad
wetland)
·
Maharashtra
- Lonar Lake, Nandur Madhameshwar, Thane Creek
·
Gujarat
- Khijadiya, Nalsarovar, Thol Lake, Wadhvana Wetland
·
Karnataka
- Ranganathittu Bird Sanctuary, Ankasamudra Bird Conservation Reserve,
Aghanashini Estuary, Magadi Kere Conservation Reserve
·
Madhya
Pradesh - Bhoj Wetland, Sakhya Sagar, Sirpur Lake, Yashwant Sagar
·
Jammu
and Kashmir - Hokera Wetland, Hygam Wetland Conservation Reserve, Shallbugh
Wetland Conservation Reserve, Surinsar-Mansar Lakes, Wular Lake
·
Odisha
- Ansupa Lake, Bhitarkanika Mangroves, Chilika Lake, Hirakud Reservoir,
Satkosia Gorge, Tampara Lake
·
Punjab
- Beas Conservation Reserve, Harike Wetland, Kanjli Wetland, Keshopur-Miani
Community Reserve, Nangal Wildlife Sanctuary, Ropar Wetland
Montreux Record: (Switzerland)
·
It
is maintained as a part of Ramsar list.
·
Register
of Ramsar wetland sites where changes in ecological character have occurred,
are occurring, or are likely to occur as a result of technological
developments, pollution or other human interference.
·
Currently,
two wetlands of India are in Montreux record- Keoladeo National Park (polluted
by agricultural pesticide), Rajasthan and Loktak Lake, Manipur.
o
Further,
Chilka lake was placed in the record but was later removed from it
Lonar Lake (Maharashtra)
·
Second
Ramsar site in Maharashtra
·
Created
by an asteroid collision with earth impact during the Pleistocene Epoch. It is
not a volcanic crater.
·
It
is a notified National Geo-heritage Monument.
·
The
oval-shaped Lonar Lake is a part of the Lonar Wildlife Sanctuary
Ashtamudi Lake (Kerala)
·
Ramsar
Site
·
Famous
for short neck clam - high export of the same
·
Large
palm-shaped (also described as octopus-shaped) water body, second only in size
to the Vembanad estuary
Kuttanad Wetland (Kerala)
·
One
of largest Ramsar sites in India.
·
This
region is designated as a Globally Important Agricultural Heritage Systems
(GIAHS).
o
3
GIAHS sites in India
§ Koraput Traditional Agriculture,
Odisha.
§ Kuttanad Below Sea Level Farming
System, Kerala.
§ Pampore Saffron Heritage, Jammu
& Kashmir.
·
The
region has the only agricultural system in India that practices rice
cultivation below sea level.
Harike wetland (Punjab)
·
Largest
wetland in northern India
·
The
wetland and the lake were formed by constructing the headworks across the
Sutlej river in 1953.
·
The
headworks is located downstream of the confluence of the Beas and Sutlej rivers
just south of Harike village.
·
Ramsar
Site.
Panchmuli lake: (Gujarat)
·
Situated
near the 182-metre tall statue of Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel in Kevadia, a major
tourist attraction, had a large number of crocodiles that posed a threat to
visitors. Thus they have been relocated
Deepor Beel: (Assam)
·
DeeporBeel
is located to the south-west of Guwahati city
·
It
is a bird sanctuary and it is an ‘Important Bird Area’ site as it is also a
shelter for migratory birds.
·
It
is a permanent freshwater lake. It is the only Ramsar site in Assam (announced
in 2002).
·
The
wetland is also used by elephants as a major corridor.
·
It
is in a former channel of the Brahmaputra River, to the south of the main
river.
·
The
beel has shrunk 35% since the 1990s.
Pong Dam: (HP)
·
WLS
and Ramsar Site
·
Pong
dam or Beas dam - artificial embankment Dam constructed across the Beas river –
the lake created by the dam is called Maharana Pratap Sagar.
·
Migratory
birds from all over Hindukush Himalayas and also as far as Siberia come here
during winter.
Sambhar Lake (Rajasthan)
·
It
is India's largest inland salt lake in Rajasthan.
·
It
is surrounded by the Aravali hills on all sides.
·
Ramsar
site.
·
It
is the source of salt production in Rajasthan
·
It
is spread over Jaipur and Nagaur districts. Some parts are also found in Ajmer.
·
The
lake is known for being a habitat for a large number of migratory species
during the winter season. It includes species like flamingos, pelicans and
waterfowls among others.
Sundarbans:
·
Sundarbans
is the largest Ramsar Site in India
·
In
2019, it was made Ramsar site. But Sundarbans delta, which lies in Bangladesh,
was accorded the status of a Ramsar site in 1992.
·
It
is a UNESCO world heritage site.
Chilika lake:
·
Chilika
Lake is the largest coastal lagoon or brackish water lagoon in Asia.
·
It
is the second largest brackish water lagoon in the world after the New
Caledonian barrier reef located in the South Pacific near Australia.
·
Chilika
is also regarded as the largest salt water lake of India
o
But
Sambhar Lake is the largest salt water inland lake of India
o
Pulicat
lake is the second-largest brackish water ecosystem in the country after the
Chilika Lake.
·
The
lake is located at the mouth of the Daya River and is fed by many other rives
like Bhargavi and Luna.
o
Daya
river is a distributary of Mahanadi river and thus Mahanadi river drains into
northern end of the lake
o
Chilika
lake is present to the south of Mahanadi river delta
·
It
is the largest wintering ground for migratory birds on the Indian subcontinent.
·
Chilika
Lake was designated the first Indian wetland of international importance under
the Ramsar Convention in 1981 along with Keolodeo National Park in Rajasthan.
·
Chilika
lake was listed in Montreux Record in 1993. Later it was removed in 2002.
·
Chilika
lake has Magarmukh mouth (Mouth of Crocodile)
·
It
is home to Irrawady dolphin, bottle-nose and humpback dolphins.
·
It
has been listed as a tentative UNESCO World Heritage site.
·
Nalabana
Island
o
Present
within Chilika lake – hosts Nalabana Bird Santuary
o
Habitat
for the largest congregation of waterfowls in India
Important protected areas:
·
Singhori
WLS – MP
·
Manjira
Wildlife Sanctuary - Telangana
·
Chinnar
Wildlife Sanctuary - Kerala
·
Kanger
Valley National Park - Chhattisgarh
·
Gugamal
National Park - Maharashtra
·
Gumti
wildlife sanctuary, Sipahijola Wildlife Sanctuary - Tripura
·
Intanki
National Park, Saramati peak - Nagaland
·
Bannerghatta
National Park, Shettihalli Wildlife Sanctuary – Karnataka
·
Karlapat
WLS - Odisha
·
Nokrek
Ridge NP and Balpakram NP – Meghalaya
·
Nongkhyllem
WLS - Meghalaya
·
Barnadi
WLS – Assam
· Asola Bhati WLS – Delhi Haryana Border (Aravalli hill range)
Marine National Parks:
·
Protected
sea or a lake
·
6
in India
o
Marine
National Park, Gujarat (Gulf of Kutch) – First in India
o
Mahatma
Gandhi Marine National Park – South Andaman
o
Gahirmatha
Marine Sanctuary, Odisha.
o
Gulf
of Mannar Marine National Park, Tamil Nadu.
o
Rani
Jhansi Marine National Park – Ritchie’s archipelago
o
Malvan
Marine Wildlife Sanctuary, Maharashtra
Biosphere Reserves in India:
·
18
biosphere reserves in India out of which 12 are part of the World Network of
Biosphere Reserves, based on the UNESCO Man and the Biosphere (MAB) Programme
list
·
World
Network – Nilgiri (First in 2000), Gulf of Mannar, Sundarbans, Nanda Devi,
Nokrek, Panchmarhi, Simplipal, Great Nicobar, Achanakumar-Amarkantak,
Agasthyamalai, Khanchendzonga, Panna (Latest in 2020)
·
India’s
biosphere reserves – Nilgiri (First in 1986), Panna (latest in 2011)
o
Remaining
six are Manas, Dihang-Dibang, Great Rann of Kutch, Cold Desert, Dibru Saikhova,
Seshachalam Hills
Dibru Saikhowa National Park
·
Feral
horses and rare Gangetic dolphin
Manas National Park – UNESCO world heritage sight
·
Rare
species – roofed turtle and pygmy hog
Mudumalai National Park: (Tamil Nadu)
·
National
Park and Tiger Reserve
·
Located
at the tri-junction of Karnataka, Kerala and Tamil Nadu; Northwestern side of
the Nilgiri Hills.
·
The
protected area is home to Indian elephant, Bengal tiger, gaur and Indian
leopard including critically endangered Indian white-rumped vulture and
long-billed vulture.
·
It
is contiguous with Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary on the West, Bandipur Tiger
Reserve on the North.
Anamalai Tiger Reserve (TN)
·
Earlier
known as Indira Gandhi WLS and NP
·
Anaimalai
hills
·
The
main tourist facilities are located in the northeast corner of the park at
"Topslip'', so named because of the local 19th century practice of sliding
timber logs down the hills from here.
Mukurthi NP: (TN)
·
It
is located in the northwest corner of Tamil Nadu bordering Kerala in the
Western Ghats.
·
It
was created to protect the endangered Nilgiri Tahr. In this regard, the park
was previously known as Nilgiri Tahr National Park.
·
It
is perhaps the only area of the Nilgiris that has not been badly affected by
conversion to exotic monoculture plantations.
·
It
is bordered by Mudumalai National Park and Silent Valley National Park.
Srivilliputhur Megamalai TR: TN
·
Megamalai
wildlife division and Srivilliputhur wildlife sanctuary/ The Grizzled Squirrel
Wildlife Sanctuary (GSWS)
·
To
protect the vulnerable grizzled giant squirrel also called Ratufa macroura.
·
Southwest
side of the tiger Reserve - Periyar Tiger Reserve in Kerala state.
·
Fifth
tiger reserve in Tamil Nadu.
·
Gives
birth to Vaigai river in Tamil Nadu and the Mullayar in Kerala.
Manakudi Conservation Reserve – TN:
·
Estuarine
landscape in Kanyakumari dist
·
Bird
Conservation Reserve
·
Fertile
ground for migratory birds - Redshank and Whiskered tern.
·
Known
for its annual Flamingo festival.
Point Calimere WLS and Bird Sanctuary – TN:
·
Famous
for its flamingos and blackbuck.
·
It
is the only site in Tamil Nadu to be declared as a Ramsar Site. Important Bird
Area.
·
It
is a South Indian coastal area famous for its unique tidal swamps, dry
evergreen forests and mangroves.
Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary (Kerala)
·
Integral
Part of Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve
·
Highest
Peak – Karottimala
·
Contiguous
to the protected areas of Nagarhole and Bandipur of Karnataka on the north-east
and Mudumalai of Tamil Nadu on the southeast
·
Rivers
– Kabini and Cherupuzha
Silent Valley National Park: (Kerala)
·
Nilgiri
Hills, at the heart of the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve.
·
River
Kunthi flows through the National Park. Periyar river doesnt flow through this
park.
·
It
has a large population of lion-tailed macaques.
·
Salim
Ali prevented the destruction of Silent Valley National Park
Eravikulam National Park: (Kerala)
·
Idukki
district of Kerala.
·
It
is home to the largest population of Nilgiri Tahr.
·
It
also has the Anai Mudi peak.
·
Chinnar
and Pambar river flows
·
Has
a fernarium – first time such a fern collection is being set up in the hill
station
o
Ferns
are part of epiphytic family; grow naturally in soilless condition
o
Plants
obtain water and nutrients through leaching from trees
Bandipur: (Karnataka)
·
TR
and NP
·
Tri-junction
area of the States of Karnataka, Tamil Nadu and Kerala.
·
Largest
protected area in Southern India. This protected area along with its adjoining
landscape constitutes the single largest wild population of Tigers in the
world.
·
Largest
habitat of wild elephants in South Asia.
·
Second
largest population of tigers after Corbett National Park
·
Dry
deciduous forest is the dominant type of biome in this protected area.
·
The
park is flanked by the Kabini River in the north and the Moyar river in the
south. The Nugu River runs through the park.
·
Recognized
as one of the Mega Biodiversity Areas in India.
Dandeli Anshi Tiger Reserve (Karnataka)
·
Kali
river and its tributaries flow through this forest. Hence it is also known as
Kali Tiger Reserve.
·
The
Tiger Reserve comprises two Protected Areas viz., Dandeli Wildlife Sanctuary
and Anshi National Park that are contiguous to each other.
·
It
is the only known tiger reserve to report frequent sightings of elusive Black
Panther
Malai Mahadeshwara Wildlife Sanctuary: (Karnataka)
·
Eastern
Ghats
·
The
sanctuary is contiguous with both Biligiri Ranganathaswamy Temple Tiger Reserve
on the western side and Sathyamangalam Reserve in Tamil Nadu on the southern
side.
·
M.M.
Wildlife Sanctuary will be the new tiger reserve after approval from the
National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) because this is a unique
geographical zone that acts as a bridge between the Western and Eastern Ghats.
Nagarhole National Park – Karnataka:
·
Previously
known as Rajiv Gandhi National Park - National Park, IBA and Tiger Reserve
·
Situated
between the Mysuru plateau in Karnataka and the Nilgiri Mountains of Tamil
Nadu.
·
Has
Bengal Tigers. It has the largest herd of Asiatic Elephant in the world. It is
under both Project Tiger and Elephant.
·
Part
of Nilgiris Biosphere Reserve
·
It
was also an exclusive hunting reserve of the kings of the Wodeyar dynasty
·
Jenu
Kurubas are the primary inhabitants of this forest area
·
KVIC
- Khadi and Village Industries Commission has proposed Project RE-HAB in
Nagarohole to reduce elephant and man conflicts using bee fencing.
Bannerghatta NP: (Karnataka)
·
Very
close to Bangalore
·
Falls
in the Kaveri basin (tributary - Arkavati) - Southeast
·
Contiguous
to the Krishnagiri and Hosur forest divisions; and the Cauvery Wildlife
Sanctuary of Karnataka
Koundinya WLS (Andhra Pradesh)
·
WLS
and an elephant reserve
·
It
is located at the tri-junction of TN, AP and Karnataka.
·
The
sanctuary has dry deciduous forests with thorny shrubs interspersed with trees.
·
It
is the only sanctuary in Andhra Pradesh with a population of Asian elephants.
From 1983 to 1986, a sizable number of elephants began their journey from the
forests of Hosur-Dharmapuri in Tamil Nadu and Anekal-Bannerghatta in Karnataka
to seek alternative homes in other regions.
Coringa WLS (AP)
·
Godavari
estuary. Coringa is a major tourist hub.
·
Yet
to become a Ramsar site
·
Has
Fishing cats
·
It
is the second-largest stretch of mangrove forests in India.
Papikonda National Park – AP
·
Papi
Hills in East Godavari and West Godavari districts of Andhra Pradesh.
·
IBA
·
The
Park lies in the River Godavari basin and Godavari river flows through this
park.
·
Vegetation
- Dry deciduous forests.
·
The
Polavaram project completion will submerge parts of the national park.
Amrabad Tiger Reserve: (Telangana)
·
Amrabad
Tiger Reserve was earlier a part of the ‘Nagarjuna sagar-Srisailam Tiger
Reserve (NSTR)’ but post-bifurcation of Telangana and Andhra Pradesh, the
northern part of the reserve is vested with Telangana state and is renamed as
‘Amrabad Tiger Reserve’. The southern portion continues to be ‘NSTR’ and is
with Andhra Pradesh.
·
Located
in the Nallamala hills of Telangana.
·
Dominated
by Chenchus - Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group from AP and Telangana.
·
Second
largest tiger reserve after the Nagarjunasagar - Srisailam Tiger Reserve in AP.
·
Lies
in the catchment of Krishna River
·
The
Telangana Forest Department has come out with a CBET (Community Based Eco
Tourism) model in the Amrabad Tiger Reserve area. The initiative would involve
the youth from the local Chenchu tribe as travel guides.
Kawal TR – Telangana:
●
Northern
Telangana
●
The Reserve is one of the richest teak forests in the state of Telangana
- Tropical Dry deciduous teak
forests mixed with bamboo constitute the predominant flora of the region.
●
Major catchment of river Godavari and local rivulets like Peddavagu and Kadam.
●
Linkages with the Tadoba-Andhari TR in Maharashtra and Indravati TR in Chhattisgarh.
●
Situated in the southernmost tip of the Central
Indian Tiger Landscape.
Panna Tiger Reserve: (MP)
·
Might
be drowned in Ken Betwa river linking project
·
Vindhyan
mountain range in northern MP
·
Last
remaining tiger habitat of North Madhya Pradesh.
·
Ken
river passes through Panna tiger reserve from south to north. Ken Gharial
Sanctuary form a significant part.
·
The
reserve is also dotted with two thousand-year-old rock paintings
·
Has
critically endangered white rumped vulture
Kanha National Park – MP
·
Tiger
Reserve
·
Nestled
in the Maikal range of Satpuras in Madhya Pradesh.
Madhav
National Park – MP
·
It
is a part of the upper Vindhyan hills. It was originally the shooting reserve
of the Maharaja of Gwalior.
·
It
was named after Madho Rao Scindia, the Maharaja of Gwalior belonging to the
Scindia dynasty of the Marathas.
·
Due
to intense hunting activity, the last of the resident wild tigers were seen in
Madhav National Park around late 1970.
·
One
male and one female tiger have once again made Madhav their home since October
2007.
·
Madhav
National Park is a part of the Ranthambhore-Kuno-Madhav (Madhya Pradesh and
Rajasthan) Tiger Corridor of Central India & Eastern Ghats landscape.
·
The
Park is currently facing displacement and rehabilitation issues as it is home
to Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) like Saharias of MP
Van Vihar NP (MP)
·
Bhopal
·
Though
it has the status of a national park, it is developed and managed as a modern
zoological park, following the guidelines of the Central Zoo Authority.
·
Animals
are kept in near-natural habitats. Most animals are either orphaned and brought
from various parts of the state or are exchanged from other zoos.
·
No
animal is deliberately captured from the forest.
Tadoba Andhari Tiger Reserve (Maharashtra)
·
Maharashtra’s
oldest and largest national park
·
River
– Andhari
·
Includes
Tadoba National Park and Andari WLS
Melghat Tiger Reserve – Maharashtra:
·
It
is among the first nine tiger reserves notified under the Tiger in 1973.
·
The
Tapi river flows through the northern end of the Melghat Tiger Reserve.
Sanjay Gandhi National Park (Maharashtra)
·
Thane
& Mumbai districts
·
The
park was named 'Krishnagiri National Park' in the pre-independence era. Later
renamed as 'Borivali National Park'. In 1981, it was re-dedicated as 'Sanjay
Gandhi National Park' in memory of Sanjay Gandhi.
·
The
park lies on the northern fringes of suburban Mumbai, India.
·
It
forms pure wilderness in the heart of Mumbai city and forms a part of the
Western Ghats biodiversity, forming roughly 20 per cent of Mumbai’s
geographical area.
·
The
park encompasses two lakes, Vihar and Tulsi, which meet part of the city’s
water requirements.
·
Situated
within the national park is an archeological complex of some 160 rock-cut caves
popularly known as the ‘Kanheri Caves’. The caves are carved from basalt rock
and date from the 1st century BCE to the 10th century CE.
o
Kanheri
is derived from Sanskrit word Krishnagiri, which literally means black
mountain.
·
Blue
Mormon butterfly (State butterfly of Maharashtra) also present in the National
park.
Satkosia Wildlife Sanctuary: (Odisha)
·
Tiger
Reserve - It is located where the Mahanadi River passes through a gorge in the
Eastern Ghats mountains.
Simlipal National Park (Odisha - Mayurbhanj):
·
Tiger
Reserve - Simlipal, which derives its name from ‘Simul’ (silk cotton) tree
·
Lies
in the eastern end of the Eastern Ghats.
·
Some
people set fire to the dry leaves of the forests to collect Mohva flowers which
are used for an addictive drink.
Bhitarkanika National Park: Odisha
·
Ramsar
site. It is not a Tiger Reserve.
·
Bhitarkanika
- estuary of Brahmani, Baitarani, Dhamra, and Mahanadi River systems.
·
Houses
70% of the country’s estuarine or saltwater crocodiles. Highest density of
saltwater crocodile in India.
·
Its
fauna includes Indian python, king cobra, black ibis, darters.
·
It
hosts many mangrove species, and is the second-largest mangrove ecosystem in
India.
·
It
also includes the Gahirmatha Marine Sanctuary as one of its three parts.
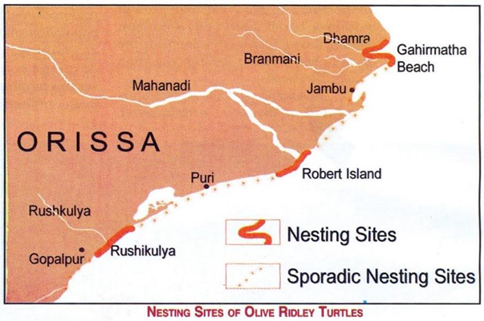
Gahirmatha Marine Sanctuary: (Odisha)
·
It
is the world's largest nesting beach for Olive Ridley Turtles and world’s
largest rookery (breeding colony) of sea turtles
·
It
extends from Dhamra River mouth in the north to Brahmani river mouth in the
south.
·
Gahirmatha
Marine Sanctuary - one of the three parts of the Bhitarkanika National Park
Ranthambore Tiger Reserve: (Rajasthan)
·
National
Park and Tiger Reserve
·
It
is bounded to the north by the Banas River and to the south by the Chambal
River.
·
It
has dense tropical dry deciduous forest, open bushland and rocky terrain
interspersed with lakes and streams.
Gir National Park
·
South-west
of the Saurashtra peninsula in the state of Gujarat.
·
The
Gir forest has the Kamleshwar Dam.
·
Except
Africa, Gir Forest is the only place in the world where one can see lions
roaming in the open.
·
It
was the kind effort of Nawabs of Junagadh who protected the lions in their own
private hunting grounds.
Blackbuck National Park, Velavadar – Gujarat
·
In
Saurashtra
·
On
the coast of Gulf of Cambay
·
was
primarily a "vidi" (grassland) of the maharaja of the princely state
of Bhavnagar for hunting the blackbucks with his famous hunting cheetahs
·
Black
buck, lesser floricans (more in this national park), wolfs
Pilibhit Tiger Reserve: Uttar Pradesh
·
The
Pilibhit Tiger Reserve and the Uttar Pradesh Forest Department bagged the first
international award TX2 for doubling its number of tigers in four years. (total
tigers 57)
·
The
target set was to double the numbers in ten years. The target was set by the
partners of the award in 2010. The partners are Global Tiger Forum, United Nations
Development Programme, Conservation Tiger Standards and Lion’s Share.
·
The
Pilibhit Tiger Reserve was chosen based on the Tiger Census conducted by the
National Tiger Conservation Authority in 2018.
·
Borders
Nepal x
Valmiki Tiger Reserve: (Bihar)
·
NP
and TR
·
India
Nepal Border – forms a continuous ecological corridor with Chitwan National
Park in Nepal
·
on
the bank of river Gandak.
·
It
is the only National Park and tiger reserve in Bihar.
·
Excellent
example of Himalayan Terai landscape – eastern most limit of Himalayan Terai
forests
Terai Arc Landscape (TAL) – protected areas from west to east
·
Rajaji
National Park in Uttarakhand – elephant population and tiger reserve
·
Corbett
National Park in Uttarakhand
·
Pilibhit
Tiger Reserve in UP
·
Dudhwa
Tiger Reserve in UP
·
Katarniaghat
Wildlife Sanctuary in UP – gharial population and critical tiger habitat
·
Sohelwa
Wildlife Sanctuary in UP
·
Valmiki
National Park in Bihar
·
TAL
recognized as one of the seven UN World Restoration Flagships in UN Decade on
Ecosystem Restoration
Kibber WLS – HP
·
Bank
of Spiti River
·
India’s
only cold desert WLS
Rajaji Tiger Reserve – Uttarakhand
·
National
Park and Tiger Reserve
·
Located
in Haridwar, along the foothills of the Shivalik range
·
This
area is the North Western Limit of habitat of Asian elephants.
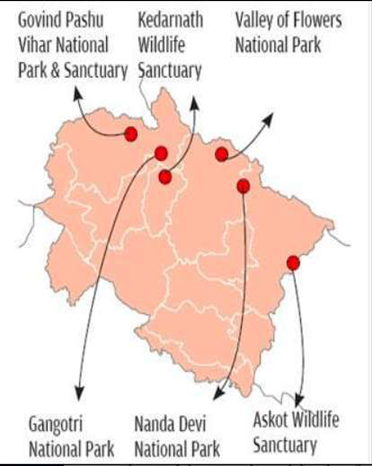
Govind Pashu Vihar National Park - Uttarakhand
·
Original name of the National Park was Tons and
later altered to Govind Pashu Vihar after a prominent Indian freedom fighter
and politician Govind Ballabh Pant.
o
The park creates an upper water catchment of
River Tons which is a significant tributary of Yamuna River.
·
Established to protect Snow Leopards.
·
The park lies in the higher reaches of the
Garhwal Himalayas.
·
The mountains in the park include Swarg Rohini,
Black Pearl and Bunder punch.
·
Snow leopard, black and brown Himalayan bear,
leopard cat, musk deer, fishing cat, thar, serow, Sambar, goral, wild boat,
etc.
·
The sanctuary contains western Himalayan
broadleaf forests at its lowest elevations, transitioning to western Himalayan
subalpine conifer forests and western Himalayan alpine shrub and meadows at its
highest elevations.
Bugun Community Reserve in Arunachal Pradesh
·
Present in Western Arunachal Pradesh near
Eaglenest Wildlife Sanctuary
·
Bugun Liocichla – endemic to India and
Critically endangered – found in Eaglenest Wildlife Sanctuary and Bugun
community reserve – temperate forest
Sultanpur National Park – Haryana
·
The area Sultanpur was named after the
descendant of Harsh Dev Chauhan, Sultan Singh.
·
The park is also named as Dr. Salim Ali Bird
Sanctuary after this famous Indian ornithologist and naturalist.
·
It is a great place for migrating birds.
(Siberian Cranes, Greater Flamingo)
Kishtwar National Park – Jammu and Kashmir
·
Temperate type – Mainly comprises Coniferous,
Alpine, Meadows and Scrub forests.
·
Snow leopards
·
Has tributaries of Chenab
·
Has Brammah mountain
Buxa Tiger Reserve (West Bengal)
·
Buxa
Hills in Bhutan’s southern hilly region. Its northern border is parallel to
Bhutan’s international border.
·
The
National Tiger Conservation Authority has designated the Buxa Tiger Reserve for
the tiger augmentation programme
Jaldapara WLS – West Bengal
·
Has the highest number of Indian one-horned
rhinoceros in West Bengal.
·
Toto tribes and Mech Tribes (Bodos) used to stay
in this area before 1800. At that time, this place was known as “Totapara”.
·
The park is situated at the foothills of the
Eastern Himalayas and on the bank of the Torsa River, right bank tributary of Brahmaputra.
The Western side of River Torsa is called the Jaldapara and the Eastern side is
known as Chilapata forests.
·
Jaldapara is one of the most popular forests of
Dooars. The Dooars valley (also called Duars) is the floodplains of Northern
Bengal and Eastern Assam. The Western Boundary of Dooars is formed by the
Teesta River, whereas its Eastern boundary within Assam is not very clearly
defined.
Transboundary Manas Conservation Area (TraMCA)
·
region
of high biodiversity that extends along south-eastern Bhutan and northeastern
India
Pobitora Wildlife Sanctuary Assam
·
Situated
on the southern bank of River Brahmaputra
·
IBA
·
Highest
density of Rhino in the world. The second-highest concentration of Rhino in
Assam after Kaziranga
·
Divided
into three distinct categories - Forest or thick tree cover - 13% Grasslands - 72% Remaining area - water bodies or beels.
·
Often
called ‘Mini Kaziranga’ due to similar landscape and vegetation.
·
Consists
of Rajamayong Reserve Forest and Pobitora Reserve Forest
Raimona National Park – Assam
·
Raimona
in western Assam
·
The
Raimona National Park is within the Bodoland Territorial Region.
·
The
area of the park includes the northern part of the notified Ripu Reserve
Forest, which forms the western-most buffer to the Manas National Park that
straddles the India-Bhutan border.
·
Raimona
was bounded on the west by the Sonkosh river along the Assam-West Bengal border
running southward from the India-Bhutan border and the Saralbhanga river on the
east till it touched the India-Bhutan border on the north and the southern part
of the Ripu Reserve Forest
Pakke Or Pakhui WLS (Arunachal Pradesh)
·
Tiger
Reserve - This Tiger Reserve has won India Biodiversity Award 2016 in the
category of 'Conservation of threatened species' for its Hornbill Nest Adoption
Programme.
·
Pakke
is a haven for hornbills in north-east India, with four of the nine species –
the Great Hornbill, the Wreathed Hornbill, the Oriental Pied Hornbill and the
Rufous-necked Hornbill- found here.
·
Towards
the south and south-east, the sanctuary adjoins reserve forests and Assam's
Nameri National Park.
·
It
is bounded by Bhareli or Kameng River in the west and north, and by Pakke River
in the east.
Mouling National Park (Arunachal Pradesh)
·
Temperate
alpine and coniferous forest at the upper reaches whereas the lower area is
covered with tropical evergreen forest.
·
Ornamental
plants like foxtail, orchids are abundant in this area.
·
Many
endangered species like takins, snow clouded leopard, golden langur, hornbill
are spotted here.
Galthea National Park: (Great Nicobar)
·
Forms
a part of Great Nicobar Biosphere Reserve, which also includes the larger
Campbell Bay National Park. This Campbell Bay is present in the eastern side of
Great Nicobar
·
Nicobarese
Megapode and Nicobar pigeon
Dugong Conservation Reserve
·
Government
of Tamil Nadu recently announced its plan to set up India’s first Dugong Conservation
Reserve in the Palk Bay on the southeast coast.
Nehru Zoological Park (Hyderabad)
·
Major
attraction lion safari
Lichen Park – Uttarakhand
·
Country’s
first lichen park in Musiyari, Uttarakhand
·
Symbiosis
of fungi and algae or cyanobacteria
Lake Natron – Tanzania
·
Salt
lake – Ramsar site
·
The
water from the lake does not drain out to any river or sea.
·
High
levels of evaporation cause sodium carbonate decahydrate (Natron salt) to be
left behind in its bed due to high temperatures. pH can reach upto 12.
·
The
lake’s warm water is an ideal breeding ground for the Rift Valley flamingos.
Galapagos islands
·
The
giant tortoises found here – ‘Galápagos’ in old Spanish– give the islands its
name.
·
UNESCO’s
first World Heritage Site.
·
It
was here that the British naturalist Charles Darwin made key observations in
1835 that shaped his theory of evolution. Darwin described the islands as a
“world in itself”.
Tiger Translocation Project
·
India’s
first inter-state Tiger translocation project was initiated in 2018 wherein two
big cats, a male (Mahavir) from Kanha Tiger Reserve and a female (Sundari) from
Bandhavgarh Tiger Reserve from Madhya Pradesh were relocated to Satkosia Tiger
Reserve in Odisha, to shore up the tiger population in the state.
·
The
relocation was meant to serve two purposes — reducing tiger population in areas
with excess tigers to majorly reduce territorial disputes, second, to
reintroduce tigers in areas where the population has considerably reduced due
to various reasons.
·
The
project ran into trouble within weeks of initiation. Subsequently, the project
was suspended by NTCA.
·
The
major reason was the lack of confidence and trust-building between the forest
department and the villagers.
Sessa orchid sanctuary – Arunachal Pradesh –
under WPA, 1972
Sea cucumber conservation area – Lakshadweep
Coral triangle
·
The
Coral Triangle (CT) is a roughly triangular area in the tropical waters around
Indonesia, Malaysia, Papua New Guinea, the Philippines, the Solomon Islands and
Timor-Leste.
·
The
Coral Triangle is located between the Pacific and Indian oceans.
·
As
one of eight major coral reef zones in the world, the Coral Triangle is
recognized as a global centre of marine biodiversity.
·
Known
as the "Amazon of the seas". It contains more than 76% of the world's
shallow-water reef-building coral species, six out of seven of the world's sea
turtle species and the world’s largest mangrove forest.
Pench Tiger Reserve
·
Pench
Tiger Reserve (PTR) in Maharashtra - India’s inaugural Dark Sky Park and the
fifth in Asia.
o
Pench
tiger reserve spans two States – Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra.
·
Dark
Sky park - areas designated for the protection of night skies from light
pollution
Changthang WLS
·
India’s
first dark-sky Reserve (not Park) is the Indian Astronomical Observatory (IAO),
a high-altitude astronomy station situated in Hanle village (part of Changthang
WLS) and operated by the Indian Institute of Astrophysics.
o
elevation
of 4,500 meters (14,764 ft), the IAO ranks among the world’s highest sites for
optical, infrared and gamma-ray telescopes.
·
Reserves
consist of a core area meeting minimum criteria for sky quality and natural
darkness, and a peripheral area that supports dark sky preservation in the
core.
·
The
land may be publicly or privately owned, provided that the landowner(s) consent
to the right of permanent, ongoing public access to specific areas included in
the DarkSky Park designation.
Tiger Reserves in India
·
55
tiger reserves (March 2024) in India which are governed by Project Tiger (1973)
which is administered by the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA).
o
Project
Tiger (1973) is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme - Spread across 18 states
o
Nine
Tiger Reserves to be declared first (1973-74) – Bandipur, Corbett, Kanha, Manas,
Melghat, Palamau, Ranthambore, Similipal, Sunderbans
·
National
Parks with most tigers
o Corbett National Park> Bandipur
National Park> Nagarhole National Park
o
Presence
of nearly 25 percent of India’s tigers outside tiger reserves
·
Madhya
Pradesh has the highest number of Tiger Reserves in India currently. (7)
·
States
without Tiger Reserve - Gujarat, Haryana, Punjab, Himachal Pradesh, Sikkim,
Tripura, Meghalaya, Manipur, Nagaland (8 sisters – Assam, Mizoram and Arunachal
Pradesh)
·
Nagarjunsagar-Srisailam
Tiger Reserve is the largest tiger reserve in India (Andhra Pradesh).
o
Amrabad
Tiger Reserve is the second largest (Telangana)
o
Bor
Tiger Reserve of Maharashtra is the smallest Tiger reserve.
·
Uttarakhand's
Corbett Tiger Reserve (CTR) has reported the highest tiger density among
India's reserves with 14 tigers per 100 sq km, followed by Kaziranga, Nagarhole
and Orang tiger reserves.
·
Conservation
Assured Tiger Standards (CATS) scheme
o
globally
accepted conservation tool that sets best practices and standards to manage
tigers.
o
It
sets minimum standards for the effective management of target species.
o
It
is being implemented in seven tiger range countries.
o
23
tiger reserves of India have received CA|TS accreditation.
·
Tiger
Corridors of India – 32 major corridors
·
Recent
tiger reserves
o
50
– Kamlang – Arunachal Pradesh – 2017
o
51
– Srivilliputhur Megamalai – TN - 2021
o
52
– Ramgarh Visdhari Tiger Reserve – Rajasthan - 2022
o
53
– Ranipur Tiger Reserve – UP - 2023
o
54
- Veerangana Durgavati Tiger Reserve – MP - 2023
o
55
– Dholpur Karauli Tiger Reserve – Rajasthan – 2023
·
Amangarh
Tiger Reserve, UP is a buffer zone of Jim Corbett National Park and may not be
regarded as a separate tiger reserve
·
Namdapha
in Arunachal – eastern most; Rajaji in Uttarakhand – northern most; Sahyadri –
Westernmost; Kalakkad Mundanthurai - Southernmost
State wise list:
·
Uttarakhand
o
Jim
Corbett Tiger Reserve
o
Rajaji
National Park
·
Uttar
Pradesh
o
Dudhwa
Tiger Reserve
o
Pilibhit
Tiger Reserve
o
Ranipur
Tiger Reserve
·
Telangana
o
Kawal
Tiger Reserve
o
Amrabad
Tiger Reserve
·
Madhya
Pradesh
o
Bandhavgarh
Tiger Reserve
o
Satpura
Tiger Reserve
o
Kanha
Tiger Reserve
o
Panna
Tiger Reserve
o
Pench
Tiger Reserve (Between Maharashtra and MP)
o
Sanjay-Dubri
Tiger Reserve
o
Veerangana
Durgavati Tiger reserve
·
Tamil
Nadu
o
Anamalai
Tiger Reserve
o
Kalakkad
Mundanthurai Tiger Reserve
o
Mudumalai
Tiger Reserve
o
Sathyamangalam
Tiger Reserve
o
Srivilliputhur
Meghamalai Tiger Reserve
·
West
Bengal
o
Buxa
Tiger Reserve
o
Sunderbans
Tiger Reserve
·
Rajasthan
o
Mukundara
Hills Tiger Reserve
o
Ranthambore
Tiger Reserve
o
Sariska
Tiger Reserve
o
Ramgarh
Vishdhari Tiger Reserve
o
Dholpur
Karauli Tiger Reserve
·
Odisha
o
Satkosia
Tiger Reserve
o
Simlipal
Tiger Reserve
·
Mizoram
o
Dampa
Tiger Reserve
·
Kerala
o
Periyar
Tiger Reserve
o
Parambikulam
Tiger Reserve
·
Karnataka
o
Bandipur
Tiger Reserve
o
Nagarhole
Tiger Reserve
o
Bhadra
Tiger Reserve
o
Anshi
Dandeli Tiger Reserve or Kali Tiger Reserve
o
Biligiri
Ranganatha Swamy Temple Tiger Reserve or BRT Tiger Reserve
·
Jharkhand
o
Palamau
Tiger Reserve
·
Bihar
o
Valmiki
National Park
·
Chhattisgarh
o
Indravati
Tiger Reserves
o
Udanti
& Sitanadi Tiger Reserve
o
Achanakmar
Tiger Reserve
o
Guru
Ghasidas National Park and Tamor Pingla Wildlife Sanctuary
·
Maharashtra
o
Melghat
Tiger Reserve
o
Pench
Tiger Reserve (Between Maharashtra and MP)
o
Tadoba
Andhari Tiger Reserve
o
Sahyadri
Tiger reserve
o
Nagzira-Navegaon
Tiger Reserve
o
Bor
Tiger Reserve
·
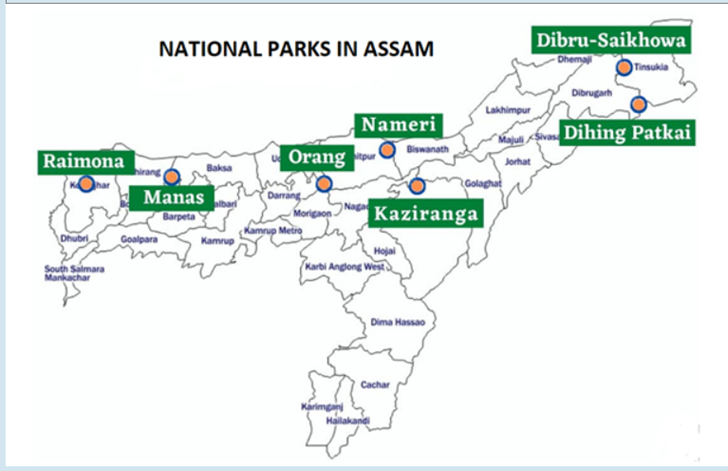
Assam
o
Kaziranga
Tiger Reserve
o
Manas
Tiger Reserve
o
Nameri
Tiger Reserve
o
Orang
Tiger Reserve
·
Andhra
Pradesh
o
Nagarjunsagar-Srisailam
Tiger Reserve
·
Arunachal
Pradesh
o
Namdapha
Tiger Reserve
o
Pakhui
Tiger Reserve
o
Kamlang
Tiger Reserve
Project Elephant – 1992
·
Elephant
reserves - 33 in 2024 spread over 10 elephant landscapes in 14 states
o
latest
addition is the Terai Elephant Reserve (TER) in Dudhwa-Pilibhit, Uttar Pradesh
and second in UP
·
Centrally
sponsored scheme
·
State
governments of elephant range states can propose conservation areas to be
declared as elephant reserves
·
Steering
committee chaired by Minister of Environment, Forest and Climate Change
approves the notification
·
Both
elephant reserves and elephant corridors are administrative classification.
Thus do not enjoy any special protection as they are not recognized by any law.
Thus governments can divert elephant reserves for various projects
Elephant Corridors
·
Strips
of land allowing elephants to move between two or more habitats
·
Ministry
of Environment, Forest and Climate Change and state forest departments identify
elephant corridors
·
2023
– 150 elephant corridors across 15 elephant range states up from 88 in 2010
·
West
Bengal has the largest number of identified elephant corridors in India
·
WPA
1972 does not specifically mention elephant corridors